Type 1 diabetes is a disease that has been known since ancient times. However, if in the times of ancient Greece and Rome, doctors did not really know what it was, and there were no methods for treating the disease, now the situation has changed for the better. Nevertheless, type 1 diabetes remains a disease to this day, which every year takes many human lives. Description
What is it – diabetes?
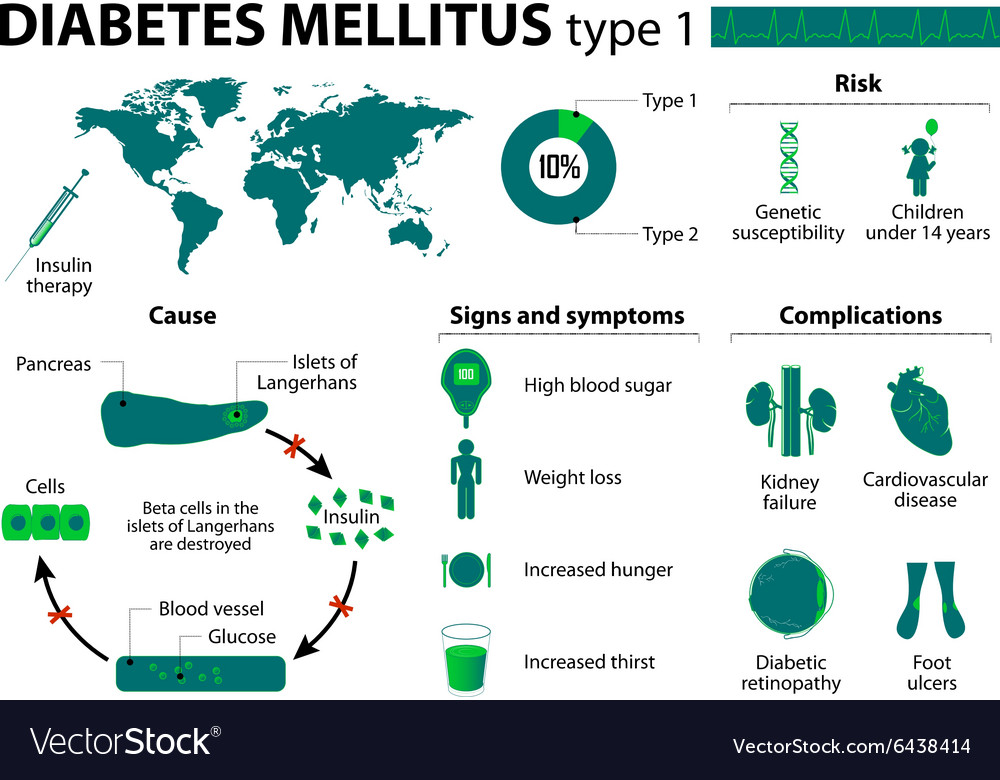
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a disease associated with the pancreas. Many do not know anything about this body, about why it is needed. Meanwhile, one of the functions of the pancreas is the production of insulin peptide, which is necessary for the processing of glucose entering the body through the gastrointestinal tract, belonging to the class of simple sugars. More specifically, insulin is produced only by part of the pancreas – the islets of Langerhans . Such islets contain several types of cells. Some cells produce insulin, the other part – an insulin antagonist, the hormone glucagon. Cells that produce insulin are called beta cells . The word “insulin” comes from the Latin insula , which means “island”.
If no insulin in the body, the glucose enters the bloodstream, it can not penetrate into various tissues, especially in muscle. And the body will lack the energy that glucose gives to it.
But this is not the main danger. “Restless” glucose, not processed by insulin, will accumulate in the blood, and as a result will be deposited both on the walls of the blood vessels themselves and in various tissues, causing their damage.
Such diabetes is called insulin-dependent. The disease affects mainly adults of young age (up to 30 years). However, there are cases when children, adolescents and the elderly fall ill.
Causes of disease
What can cause insulin to stop? Although people have been researching diabetes for more than 2,000 years, the etiology, that is, the root cause of the disease has not been reliably determined. True, there are various theories about this.
First of all, it has long been established that many cases of diabetes mellitus of the first type are caused by autoimmune processes. This means that pancreatic cells are attacked by their own immune cells and as a result are destroyed. There are two main versions why this happens. According to the first, due to the violation of the blood-brain barrier, the lymphocytes, which are called T-helpers, interact with the proteins of the nerve cells. Due to the malfunctioning of the recognition system of foreign proteins, T-helper cells begin to perceive these proteins as proteins of a foreign agent. By an unfortunate coincidence, the beta cells of the pancreas also have similar proteins. The immune system turns its “anger” on the cells of the pancreas, and destroys them in a comparatively short time.
Viral theory tends to give a simpler explanation of the causes of the attack of lymphocytes on beta cells – the effects of viruses. Many viruses are capable of infecting the pancreas, such as rubella viruses and certain enteroviruses ( Coxsackie viruses ). After the virus settles in the beta cell of the pancreas, the cell itself becomes a target for lymphocytes and is destroyed.
Perhaps in some cases of diabetes mellitus type 1 there is one mechanism of the development of the disease, and in some cases the other, and perhaps both of them contribute. But often the root cause of the disease is impossible to establish.
In addition, scientists have found that diabetes mellitus is often caused by genetic factors, which also contribute to the appearance of the disease. Although the hereditary factor in the case of type 1 diabetes is not as clear as in the case of type 2 diabetes. However, genes have been found whose damage can trigger the development of type 1 diabetes.
There are other factors contributing to the development of the disease:
- reduced immunity
- stresses
- unhealthy diet
- other diseases of the endocrine system,
- thin body build
- alcoholism,
- tobacco smoking .
Sometimes diabetes of the 1st type can be caused by pancreatic cancer and poisoning.
Stages and progression of the disease
Unlike type 2 diabetes, which develops slowly over a period of several years, type 1 diabetes goes to a severe stage within a month, or even 2-3 weeks. And the first symptoms that indicate a disease usually manifest violently, so that they are hard to miss.
In the very first stages of the disease, when the immune cells are just beginning to attack the pancreas, clearly visible symptoms in patients are usually absent. Even when 50% of the beta cells are destroyed, the patient may not feel anything, except perhaps a slight indisposition. But the real manifestation of the disease with all its characteristic symptoms occurs only when approximately 90% of the cells are destroyed. With this extent of the disease, the remaining cells cannot be saved, even if the treatment is started on time.
The last stage of the disease is the complete destruction of the cells that produce insulin . At this stage, the patient can no longer do without insulin injections.
Symptoms
Diabetes of the first type is in many ways similar in its symptoms to type 2 disease. The only difference is the intensity of their manifestation and the sharpness of the onset of the disease.
The main symptom of diabetes is frequent urination associated with acute thirst. The patient drinks a lot of water, but it creates the feeling that the water in it does not linger.
Another characteristic symptom is sudden weight loss. Usually, people with a thin physique are ill with type 1 diabetes, but after the onset of the disease a person can lose several more kilograms.
Initially, the patient’s appetite increases, as the cells lack energy. Then the appetite may decrease as the body becomes intoxicated.
If the patient has such symptoms, then he should immediately consult a doctor.
Complications
The increase in blood glucose is called hyperglycemia. Hyperglycemia entails such serious consequences as violations of the kidneys, brain, nerves, peripheral and main vessels. The level of cholesterol in the blood may increase. The defeat of small vessels often leads to ulcers, dermatitis. Retinopathy may develop , resulting in blindness.
Severe, life-threatening complications of type 1 diabetes include:
- heart attack
- stroke
- ketoacidosis,
- coma,
- gangrene of the limbs,
Ketoacidosis is a condition caused by poisoning with ketone bodies, primarily with acetone. Ketone bodies occur when the body begins to burn fat reserves in order to extract energy from fat.
If complications do not kill a person, they can make him disabled. However, the prognosis of type 1 diabetes without proper treatment is poor. Mortality reaches 100%, and the patient can live on the force of a year or two.
Hypoglycemia
This is a dangerous complication of type 1 diabetes. It is typical for patients undergoing insulin therapy. Hypoglycemia occurs when the glucose level is below 3.3 mmol / l. It can occur when eating habits are violated, excessive or unplanned physical activity, or insulin dosage is exceeded. Hypoglycemia is dangerous with loss of consciousness, coma and death.
Diagnostics
Usually, the symptoms of the disease are difficult to confuse with something else, so the doctor in most cases can easily diagnose diabetes. However, it is sometimes possible to confuse type 1 diabetes with its counterpart – type 2 diabetes, which requires a slightly different approach to treatment. There are also rare borderline types of diabetes that have a set of signs of both type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes.
The main diagnostic method is a blood sugar test. Blood analysis is usually taken on an empty stomach – from a finger, or from a vein. A urine sugar test, glucose load test, and glycated hemoglobin analysis may be prescribed . To determine the state of the pancreas is an analysis of C-peptide.
Treatment of type 1 diabetes
Therapy is carried out only under the supervision of an endocrinologist. Currently, treatment of type 1 diabetes can be the only method – with the help of insulin injections. All other methods are auxiliary.
Insulin therapy for diabetes
There are several types of insulin depending on the speed of action – short, ultra-short, medium and long-acting. Insulins differ in origin. Previously, insulin was mainly obtained from animals – cows, pigs. Now, however, mostly distributed insulin, obtained by genetic engineering . Long-acting insulins must be injected either twice a day or once a day. Short-acting insulins are administered immediately before a meal. The dosage should prompt the doctor, as it is calculated depending on the weight of the patient and his physical activity.
Insulin is introduced into the blood by the patient himself or by the person serving him with the help of syringes or syringes-pens. Now there is a promising technology – insulin pumps. This is a design that attaches to the patient’s body and helps get rid of manual insulin intake.
Complications of the disease ( angiopathy , nephropathy, hypertension, etc.) are treated with medications that are effective against these diseases.
Diabetes Diet
Another method of treatment is diet. Due to the constant supply of insulin with insulin-dependent diabetes, no such severe restrictions are required as with diabetes mellitus type 2. But this does not mean that the patient can eat whatever he pleases. The purpose of the diet is to avoid sharp fluctuations in blood sugar levels (both upward and downward). It must be remembered that the amount of carbohydrates entering the body must match the amount of insulin in the blood and take into account changes in insulin activity depending on the time of day.
As with type 2 diabetes, the patient must avoid foods that contain fast carbohydrates – refined sugar, confectionery. The total amount of carbohydrates consumed must be strictly metered. On the other hand, when the compensated insulin dependent diabetes, blended with insulin, can not sit on a grueling low-carbohydrate diets, especially the extreme lack of carbohydrates increases the risk of hypoglycemia – a condition in which the blood glucose level falls below the level of threatening the life.
Physical exercise
Exercise can also be beneficial in diabetes. They should not be too long and exhausting. When hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia (blood glucose level of more than 15 mmol / l) exercise is prohibited.
Self control
The patient should monitor their blood sugar levels every day. Portable ones can be useful here. glucometers with test strips. It is important to use high-quality devices and use strips with unexpired shelf life. Otherwise, the results may differ significantly from the real ones.